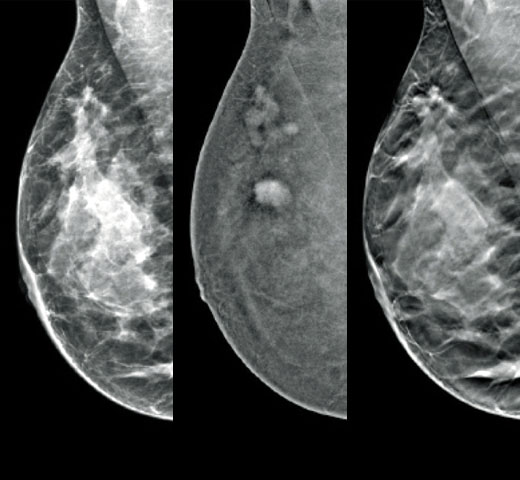
Quantra™ Technology
Standardising breast density analysis with machine learning at the point of care.
Information Exclusively Intended for Healthcare Professionals
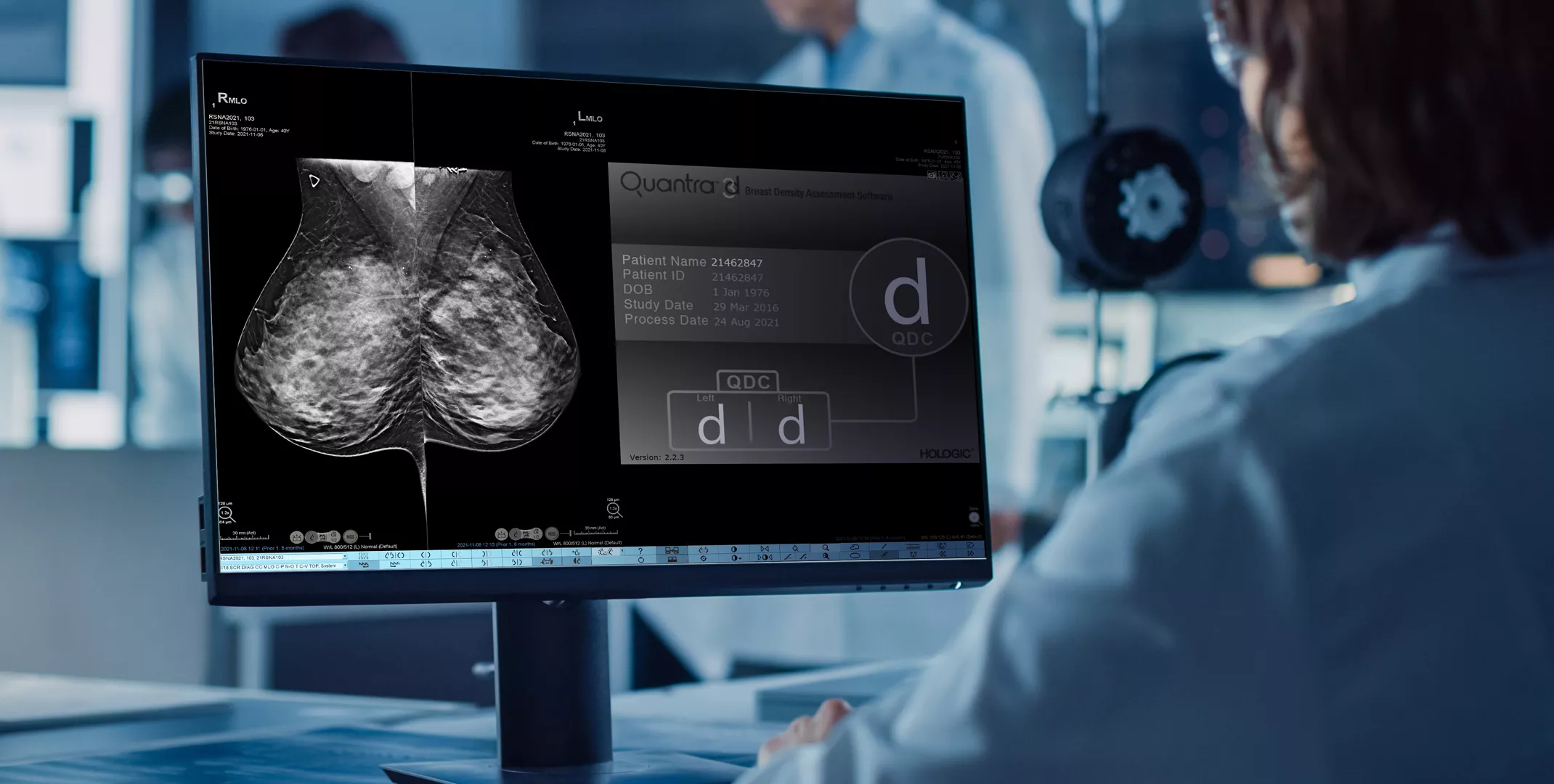
Standardise Breast Density Analysis
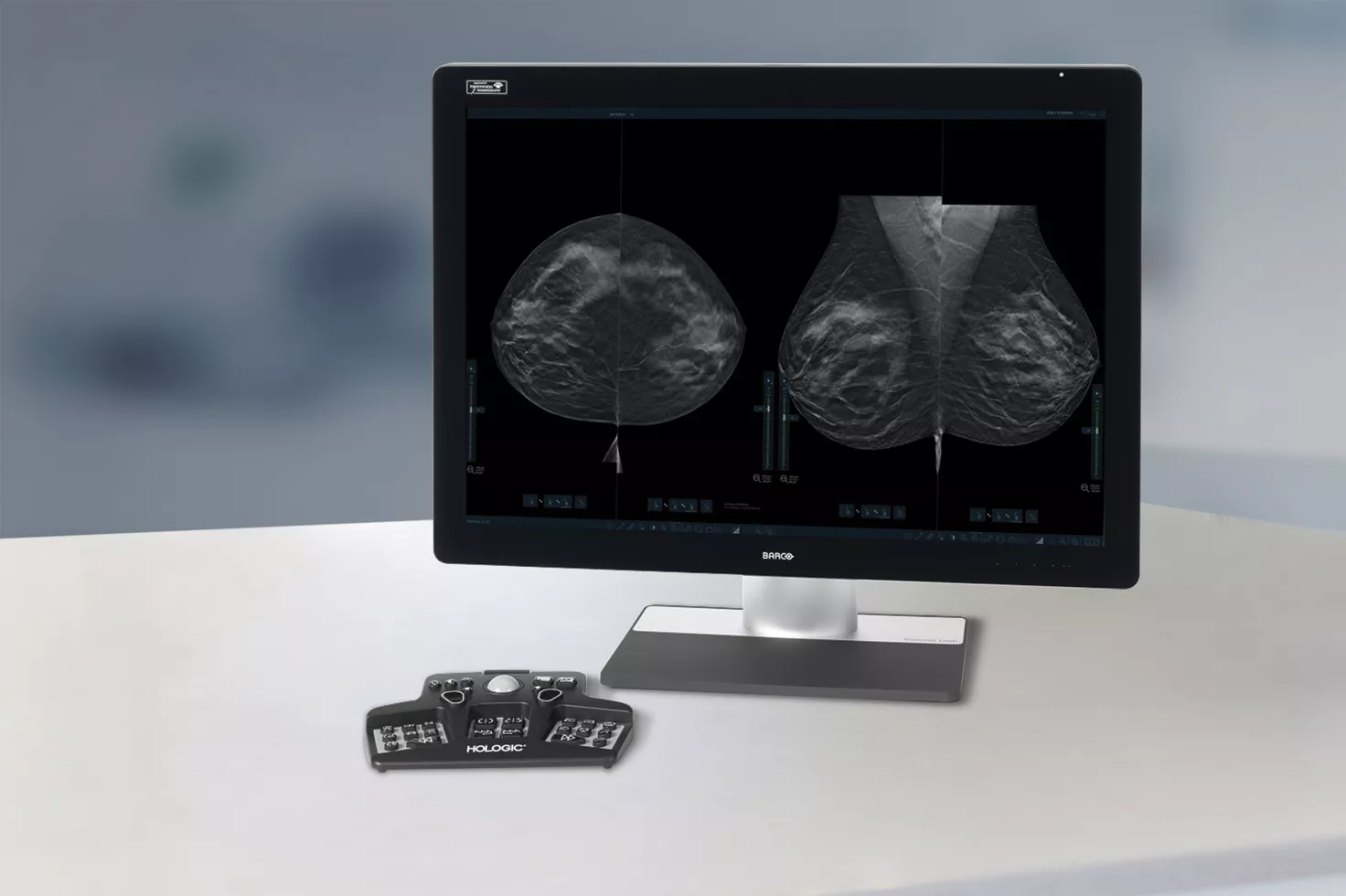
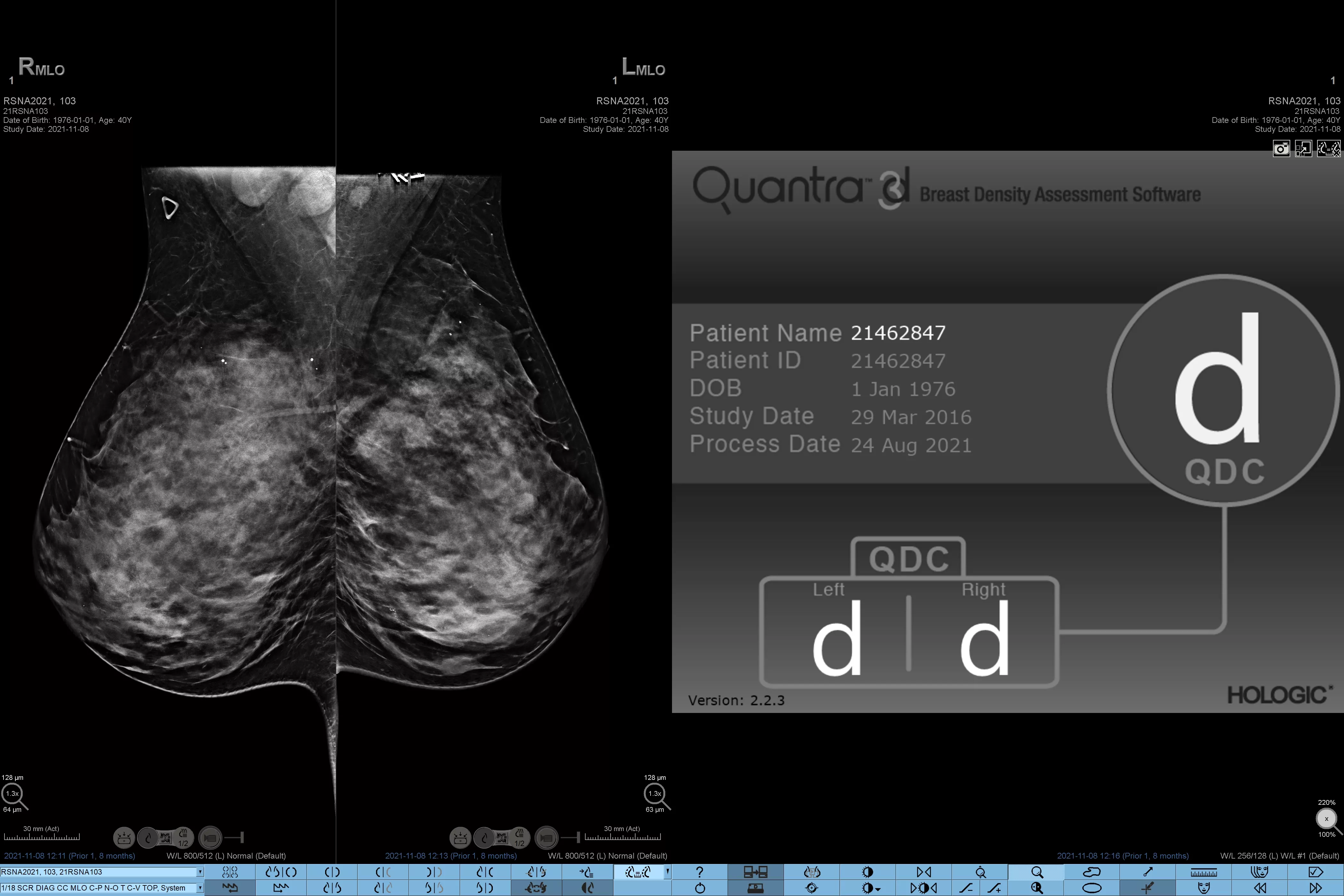
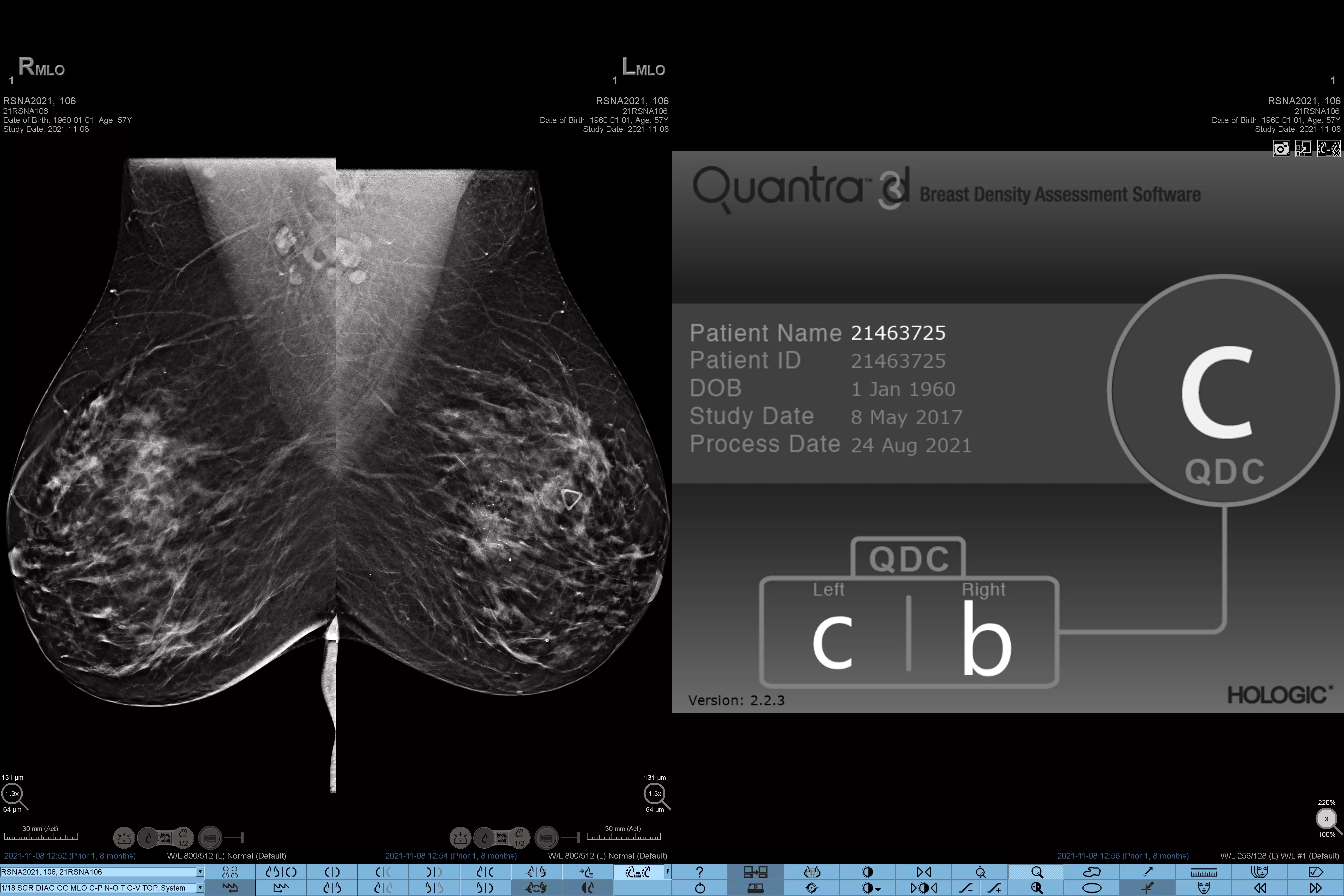
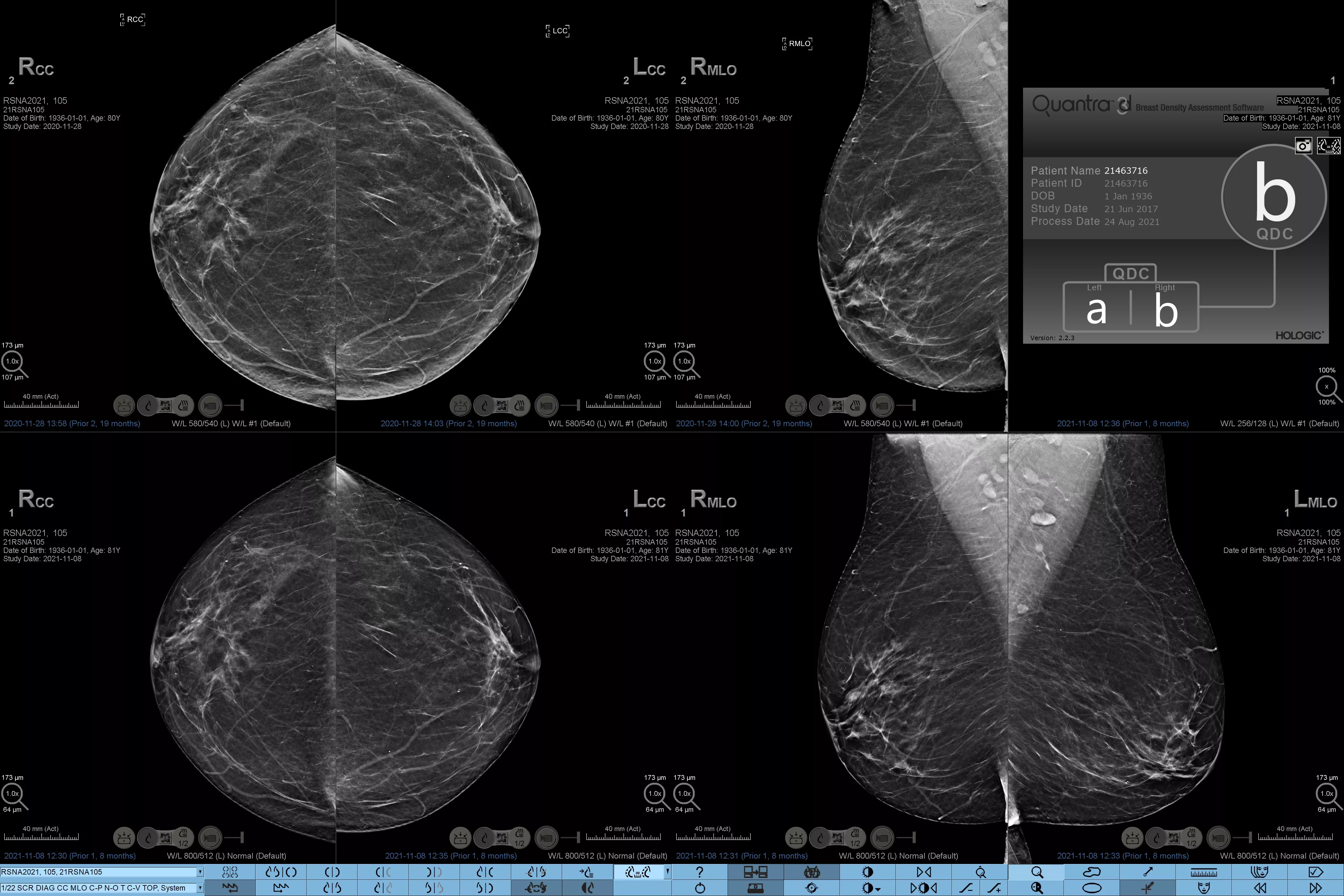
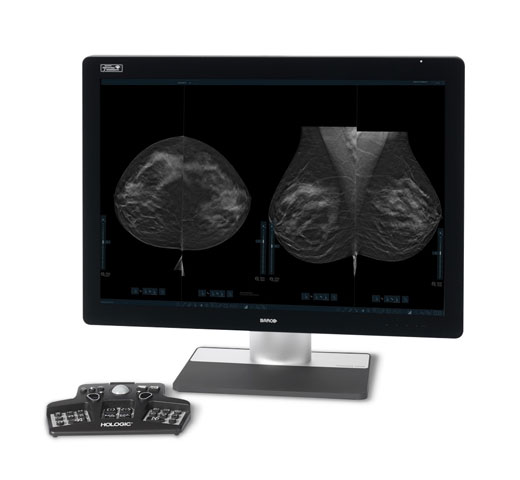
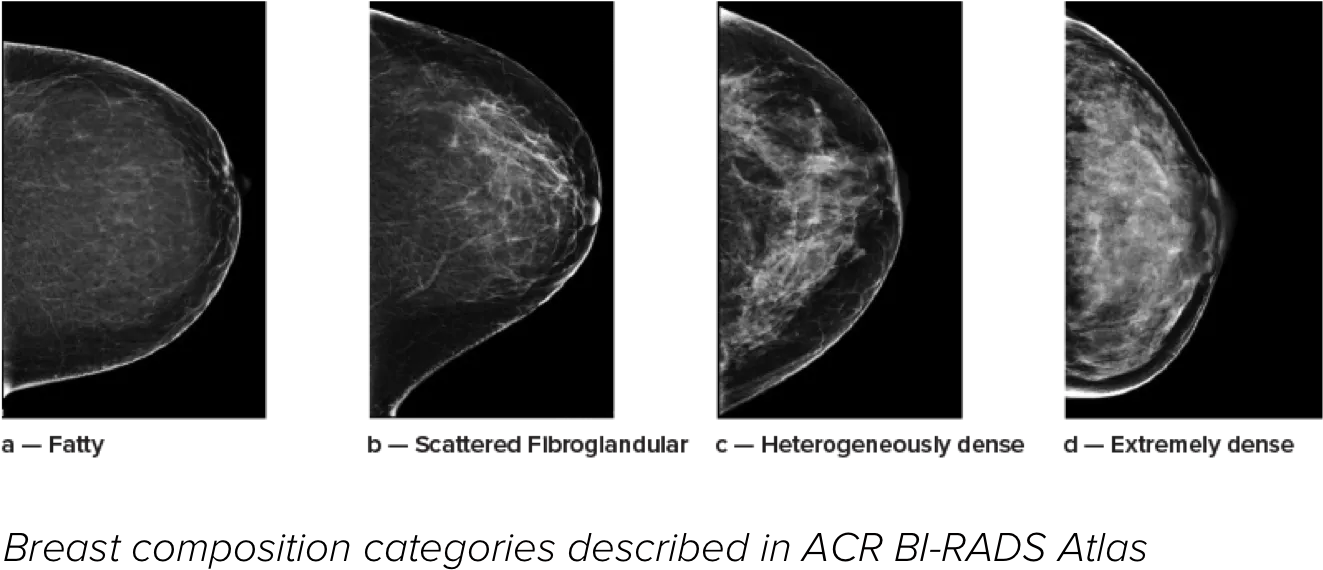
Higher breast density is known to increase a woman’s risk for breast cancer.1 The need for accurate, unbiased analysis is therefore critical. Powered by machine learning, Quantra technology software analyses both 2D™ and tomosynthesis images for distribution and texture of parenchymal tissue. It categorises breasts in four breast composition categories consistent with guidance from the American College of Radiation (ACR) BI-RADS Atlas 5th Edition.2
Better Risk Prediction
In addition to volume, pattern and texture of fibroglandular tissue may play just as an important role in mammographic cancer risk prediction.3-5 By analysing and categorising breast texture and pattern, our technology can deliver the accurate information you need to achieve more consistent and reliable scoring and confidently design patient-specific screening.
Unbiased Assessment
Objective machine learning algorithm that assigns breast density category based on analysis of breast tissue texture and patterns.
Standardisation
Provide a high standard of care and standardise reporting across the whole radiology practice.
Smoother Patient Pathway
Displays density on the acquisition workstation to facilitate patient management protocols for potential supplemental imaging.
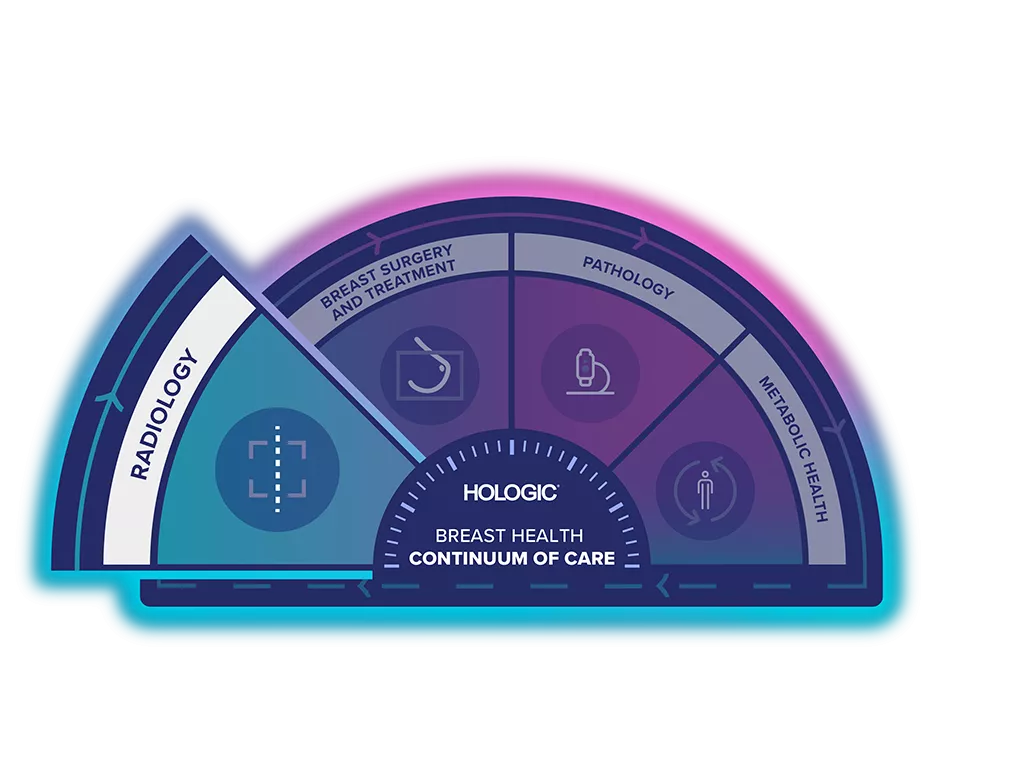
Unlock the Advantage of Time
The Breast Health Continuum of Care offers integrated solutions for clinical confidence, workflow efficiency and compassionate patient care. It is our purpose to help more women to be in better health.
Quantra Technology is part of the Hologic Screening & Diagnosis Solution.
Design Intent & Clinical Performance
Quantra software’s unbiased algorithm analyse both 2D and tomosynthesis images to support your analysis by:
- Overcoming subjectivity in visual assessment, providing more consistent, and more reliable scoring.*
- Elevating the standard of care and standardises reporting.
- Facilitating patient management protocols for supplemental imaging.
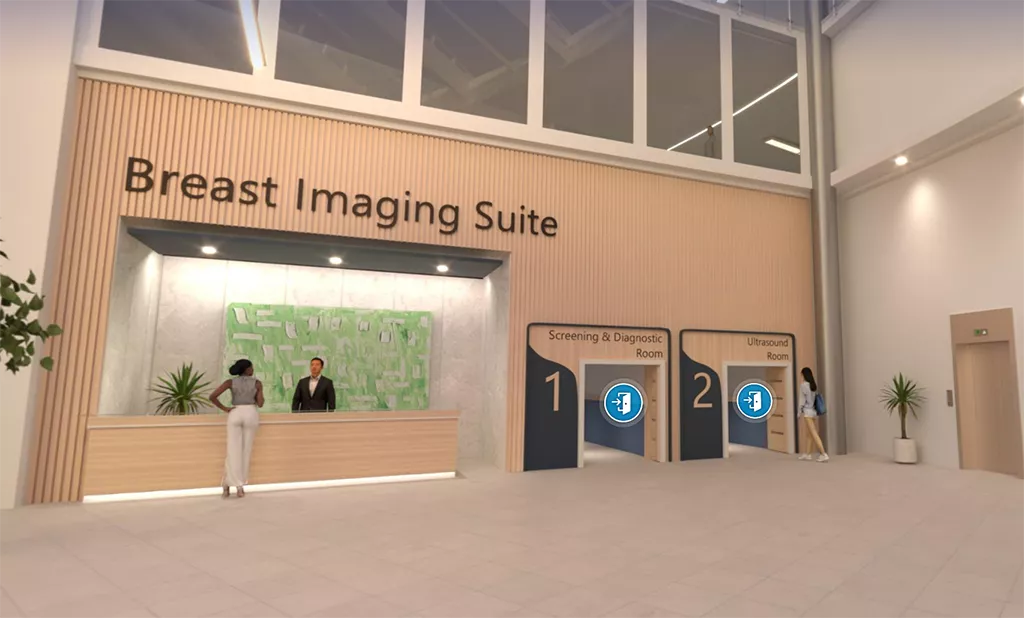

Visit Our Virtual Hospital
Browse our portfolio of Breast Health solutions in 3D. See how you can unlock the advantage of time across the entire Breast Continuum of Care.
Hologic AI-powered Integrated Software Solutions
Our products are designed to work together and can be customised to your needs. Our suite of integrated, future-proofed AI solutions is designed to improve early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer, help to accelerate workflow, and enable personalised patient care with automated breast density assessment. Discuss your clinical needs with our experienced team to find the best solution that suits you.
Risk Categories8
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
*Scores are based on ACR BI-RADS categories, in line with the revised guidance by the American College of Radiation (ACR) BI-RADS Atlas 5th Edition. This accounts for pattern and texture, compared with volume, when determining density.
**Based on 8 hours of image interpretation time per day.
Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using Tomosynthesis and Digital Mammography in Dense and Nondense Breasts. JAMA. 2016 Apr 26;315(16):1784-6.
ACR BI-RADS Atlas, 5th Edition. 2013 Available at - https://www.acr.org/Clinical-Resources/Reporting-and-Data-Systems/Bi-Rads - (Accessed on: Nov 2019)
Zuley M, Guo B, Catullo V, et al. “Comparison of Two-dimensional Synthesized Mammograms versus Original Digital Mammograms Alone and in Combination with Tomosynthesis Images.” Radiology. 2014 Jun;271(3):664-71. Epub 2014 Jan 21
Durand M, Raghu M, Geisel J, et al. “Synthesized 2D Mammography + Tomosynthesis: Can We See Clearly?” (paper presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Chicago, Il, December 2015).
Choi J, Han B, Ko E, et al. “Comparison with Two-Dimensional Synthetic Mammography Reconstructed from Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and Full Field Digital Mammography for the Detection of T1 Breast Cancer.” European Radiology. 2016 Aug;26(8):2538-46. Epub 2015 Dec.
Hologic data on file: DHM-08611 Rev 006.
Data on File: Clinical Study Report CSR-00116 Rev 004.
Breast composition categories as described in ACR BI-RADS Atlas.